How to Backup WordPress Manually: Files + Database (2026 Guide)
Learn how to manually backup your WordPress site step by step. Copy files via FTP, export your MySQL database, verify backups, and store them safely — no plugin required.

Manual backups give you full control of your WordPress site. This guide walks through backing up files and database without relying on plugins.
What a complete backup includes
You need both:
- Files: WordPress core, themes, plugins, and uploads (especially
/wp-content/) - Database: posts, pages, settings, users, and plugin data
If you only back up files, you lose content and settings. If you only back up the database, you lose themes, plugins, and media.
Before you start
Have these ready:
- SFTP/FTP or hosting file manager access
- Database access (phpMyAdmin or similar)
- A local folder with enough free space
If your site is large, plan 30 to 60 minutes for downloads.
Tip: note the file sizes in a quick text file so you can spot a bad backup later.
Step 1: Back up your WordPress files
Option A: SFTP/FTP (most reliable)
- Connect to your server with SFTP/FTP.
- Navigate to your WordPress root (often
public_html). - Download the entire WordPress directory to your computer.
Option B: Hosting file manager (faster for large sites)
- Open File Manager in your hosting panel.
- Select the WordPress root folder.
- Compress it into a
.zipfile. - Download the
.zipto your computer.
Tip: Ensure /wp-content/uploads/ is included. This folder holds all media files.
Step 2: Export your WordPress database
Using phpMyAdmin
- Open phpMyAdmin in your hosting panel.
- Select your WordPress database.
- Click Export.
- Choose Quick and SQL.
- Click Go to download the
.sqlfile.
Using WP-CLI (if available)
wp db export wordpress-backup.sql
Step 3: Verify the backup
Do a quick sanity check:
- The files download completed without errors
- The
.sqlfile opens and includesCREATE TABLElines - File sizes look reasonable for your site
If possible, test a restore on a staging site. A backup is only useful if it restores cleanly.
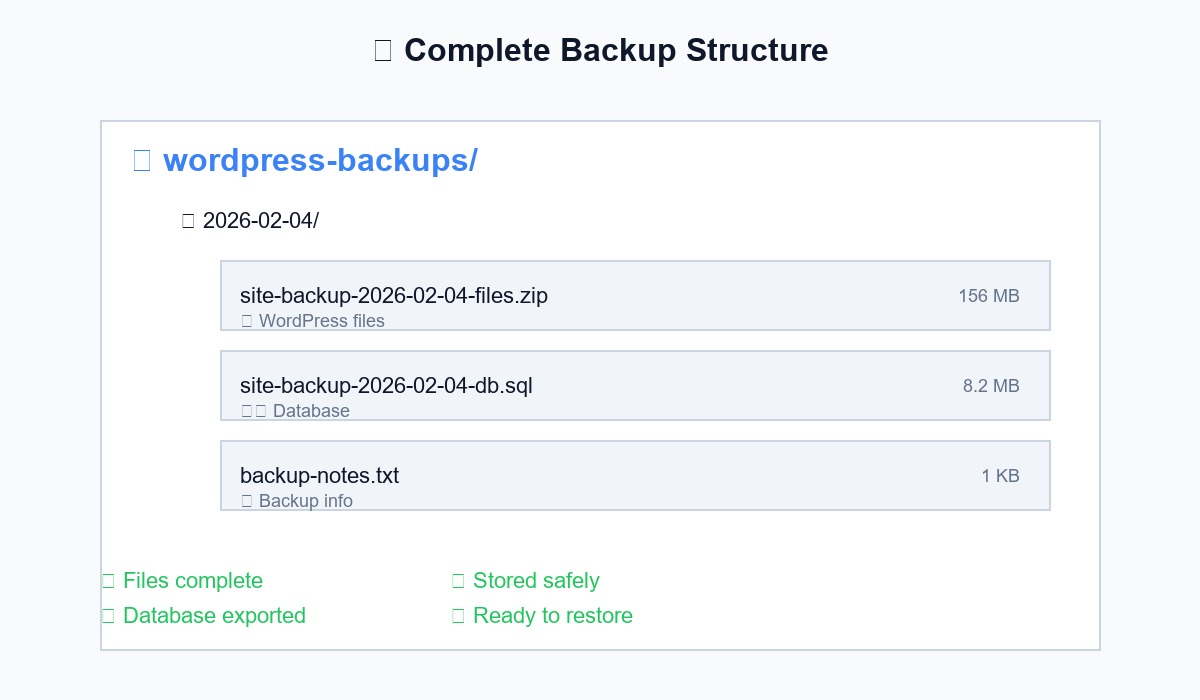
Step 4: Store backups safely
Use a simple 3-2-1 approach:
- Keep 3 copies of your backup
- Store them on 2 different types of storage
- Keep 1 copy off-site (cloud storage or external drive)
Use clear file names like:
site-backup-2026-01-15-files.zip
site-backup-2026-01-15-db.sql
Step 5: Quick restore outline
If you ever need to restore:
- Upload the files to the server.
- Create a new database and import the
.sqlfile. - Update
wp-config.phpwith the new database credentials. - If the domain changed, run a search and replace for the old URL.
Step 6: Test a restore (optional but powerful)
If possible, restore the backup to a staging site:
- Confirm the homepage loads
- Log in to the admin dashboard
- Check images and media files
- Validate a few posts and pages
Testing once gives you confidence the backup actually works.
Optional: add a simple backup schedule
Manual backups are great before major changes, but you can also schedule a reminder:
- Weekly for active sites
- Monthly for mostly static sites
- Always before a big update or redesign
Consistency reduces panic when something goes wrong.
Keep backups secure
Backups contain sensitive data. Store them in a secure location and avoid leaving them publicly accessible on the server.
Use clear file names with dates so you can find the right backup quickly. Store a copy off-site so a server failure does not wipe everything. Cloud storage is a simple option.
Common mistakes to avoid
- Backing up only
/wp-content/uploads/ - Forgetting the database export
- Storing backups on the same server
- Never testing a restore
How often should you back up?
- Active sites (daily updates): weekly file backup, daily database backup
- Mostly static sites: monthly full backup
- Before big changes: always take a full backup
Implementation checklist
When you build or update a WordPress page like How to Manually Back Up a WordPress Site (Files + Database), use this checklist:
- Create changes on staging first.
- Keep CSS and JS scoped to the template.
- Compress images and avoid unnecessary script loads.
- Test the page on mobile and desktop.
- Validate forms, emails, and admin workflows.
This avoids regressions and keeps performance stable.
Performance considerations
WordPress pages become slow when too many assets load globally. For performance:
- Load scripts only on the page that needs them.
- Avoid heavy font imports for single pages.
- Use optimized images and set explicit sizes.
- Minimize third-party widgets on conversion pages.
These small choices can make a large difference in Core Web Vitals.
Security and stability tips
Even non-sensitive pages should be built safely:
- Keep plugins and themes updated on a regular schedule.
- Use least-privilege accounts for editors and contributors.
- Back up before large template changes.
- Avoid storing sensitive data in plain text.
Stable workflows prevent emergency fixes later.
Troubleshooting guide
If something breaks after launch, check these first:
- Plugin conflicts (disable one-by-one on staging).
- Caching issues (clear server and plugin caches).
- Broken scripts (check browser console for errors).
- Missing assets (verify file paths and permissions).
A methodical check saves hours of guesswork.
QA before launch
Use this quick QA pass before you publish:
- All links and buttons work as expected.
- Forms submit and send confirmations.
- Layout looks correct on mobile.
- Images load quickly and are optimized.
- Any new admin tools are accessible and secure.
This keeps the release clean and professional.
A practical build plan you can reuse
When you tackle a WordPress project like How to Manually Back Up a WordPress Site (Files + Database), a short plan prevents scope creep:
- Map the layout and flow before touching code.
- Decide which parts belong in a template vs a builder.
- Scope scripts and styles to the page.
- Add data handling and admin tools last.
- QA on mobile, then desktop, then in admin.
This keeps the build focused and reduces cleanup later.
Content + performance balance
WordPress pages can be rich without becoming heavy:
- Keep animations subtle and avoid large libraries.
- Prefer SVG or compressed images when possible.
- Load scripts only where needed.
- Minimize inline styles that scale across the site.
The goal is a polished experience that stays fast on mobile.
Maintenance after launch
Launch is not the end. A light maintenance routine keeps pages healthy:
- Test forms and CTAs monthly.
- Re-check page speed after plugin updates.
- Audit admin tools for unused data.
- Keep backups and a rollback plan ready.
This prevents small issues from becoming expensive fixes.
Plugin vs custom code decisions
For WordPress projects like How to Manually Back Up a WordPress Site (Files + Database), decide early whether a plugin is enough:
- Use a plugin when the workflow is standard and maintenance needs to be simple.
- Use custom code when performance, UX control, or data handling requires precision.
- Hybrid approaches often work best: a plugin for baseline features, custom code for the key UX.
This avoids rebuilds later.
Accessibility and UX checks
Before launch, verify a few UX basics:
- Form labels are clear and connected to inputs.
- Buttons have descriptive text.
- The layout remains usable on small screens.
Small accessibility fixes can improve completion rates and reduce support issues.
Documentation note
Add one short note for future you:
- Where the template lives
- Which files control styling and logic
A tiny note saves time later.
One more quick win
Before you publish How to Manually Back Up a WordPress Site (Files + Database), do one more sweep:
- Compress any large images.
- Remove scripts that load on every page.
- Double-check mobile spacing and buttons.
These small fixes improve speed and usability without extra work.
FAQ
Do I need to back up WordPress core files?
Not required, but it is safer to back up the full directory. Core files can be reinstalled, but a full backup is faster.
Should I exclude cache folders?
You can exclude cache folders to reduce file size, but do it only if you know the cache can be safely rebuilt.
Is manual backup better than a plugin?
Manual backups are reliable and simple, but plugins add automation. Use manual backups at least before major updates.
Manual backups take a bit longer than plugins, but you get full control and a reliable safety net.
Frequently asked questions
How often should I back up my WordPress site?
Back up daily if you publish frequently, or weekly for less active sites. Always create a backup before updating WordPress, themes, or plugins.
What files do I need to back up in WordPress?
Back up your entire wp-content folder (themes, plugins, uploads), wp-config.php file, .htaccess file, and your MySQL database for a complete backup.
Can I back up WordPress without a plugin?
Yes. Download files via FTP/SFTP and export the database using phpMyAdmin or MySQL command line. This gives you a complete manual backup without plugin dependencies.
About the Author
Shoaib Zain
We test themes, plugins, and performance tactics to publish clear, trustworthy guides for WordPress and content sites.
Read more about us

